How To Use Data-Driven Retrospectives For Your Business
Source: Pexels
Are you ready to take your business strategies to the next level? In today's data-driven world, retrospective analysis is key to optimizing performance and promoting continuous improvement. By creating a collaborative environment that prioritizes data, organizations can unlock new insights and drive more effective decision-making.
If you're looking to harness the power of data-driven retrospectives, look no further! This article is your comprehensive guide, complete with real-world examples and best practices to help you get the most out of your business data.
Facilitating Retrospective Meetings
A retrospective meeting is a gathering where a team reflects on a recent project or work period, with the goal of identifying successes, challenges, and opportunities for improvement. Often used in Agile methodologies, this type of meeting promotes continuous improvement and collaboration among team members.
By sharing feedback and insights, teams can create actionable plans to optimize performance and achieve better results in the future. Retrospective meetings are essential for:
Enhancing Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration among team members are vital for success (Forbes). Retrospectives create a platform for team members to share their experiences, discuss challenges, and brainstorm solutions together.
Improving Transparency and Building Trust
Retrospectives help to improve transparency within the team by openly discussing successes, failures, and areas for improvement. This open dialogue fosters trust among team members and creates a supportive environment.
Early Identification of Issues and Process Improvements
Regular retrospective meetings allow teams to identify issues and potential improvements early, preventing small problems from escalating into larger ones. This proactive approach helps teams to adapt and stay ahead of the curve.
Encouraging Continuous Learning and Development
Retrospectives facilitate continuous learning and development by focusing on iterative improvement. Teams can reflect on their performance, learn from their mistakes, and identify areas for growth.
Setting up Data-Driven Retrospectives
To set up a data-driven retrospective, follow these steps:
Establish a Regular Schedule
Consistency is key when it comes to retrospectives. Establish a regular schedule, such as bi-weekly or monthly, to ensure that team members have the opportunity to reflect and improve continuously.
If a regularly-scheduled retro isn’t going to fit your team’s schedule, or just doesn’t make sense for your particular group, it’s still important to establish a consistent approach. Many teams utilize retrospectives after every project, and to make them successful (and repeatable), they consistently hold them after a pre-determined amount of time.
Whether it’s 1 day, 1 week, or 1 month post-project (some teams do all 3!) - repeating your review and reflection meetings on a consistent basis will encourage critical thinking from start to finish of every project.
Choose a Retrospective Format
Select a retrospective format that best suits your team's needs. Examples include:
Rose, Bud, Thorn: This format encourages team members to discuss what went well (rose), areas for growth (bud), and challenges (thorn).
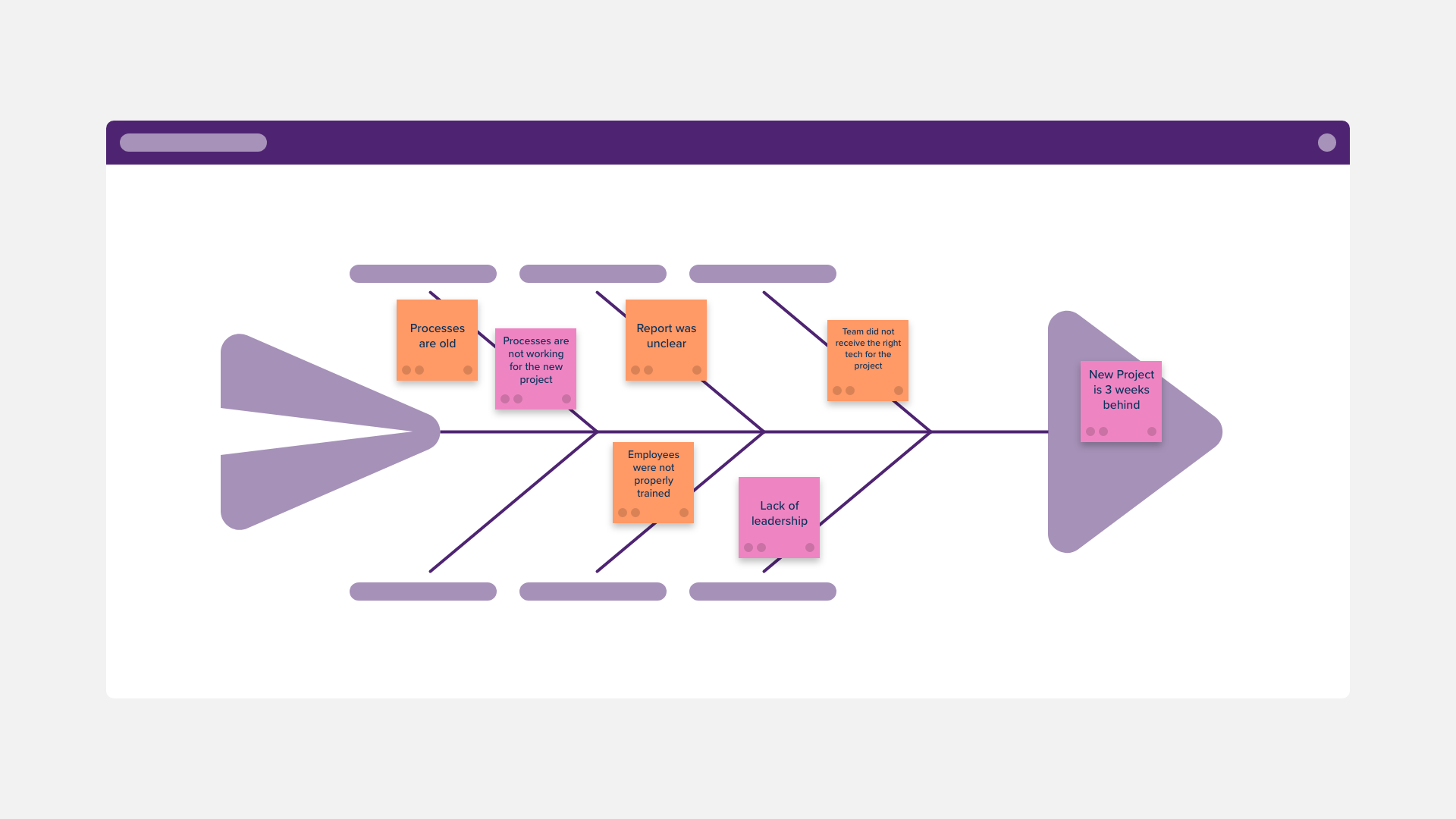
Ishikawa diagrams: Also known as fishbone diagrams, these help teams identify the root causes of a problem or issue.
Identify Key Stakeholders
Determine which team members should participate in the retrospectives. Include individuals with diverse perspectives and roles to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the team's performance.
Define Clear Objectives and Goals
Establish clear objectives and goals for each retrospective, such as identifying bottlenecks in a process or discussing ways to improve team collaboration. This focus will help to guide the conversation and ensure a productive meeting.
Collect Relevant Data
Gather pertinent data to inform the discussion during the retrospective. This data may include performance metrics, customer feedback, or team member input. Providing data-driven insights will enable the team to make informed decisions and recommendations.
Analyzing Data in Retrospectives
When analyzing data in retrospectives, it is crucial to start by employing quantitative analysis techniques. This includes descriptive statistics, which summarize and describe the main features of a dataset, such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation.
Inferential statistics help make inferences and predictions about a larger population based on a sample of data, using techniques like regression analysis and hypothesis testing. Additionally, data visualization is essential for using graphical representations like bar charts, line charts, and heat maps to illustrate patterns, trends, and relationships in data.
Following this, analyze performance metrics and KPIs. Track revenue growth over a specific period, such as quarterly or annually, to measure the success of sales and marketing efforts. Calculate customer acquisition costs to identify opportunities for optimization. Measure conversion rates and assess customer retention rates to evaluate customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Lastly, examine business trends and patterns. This involves identifying seasonal fluctuations, monitoring market changes, and evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of competitors to uncover opportunities for differentiation and growth.
Utilizing Soft Data
When utilizing soft data, begin by gathering qualitative feedback from team members. Conduct one-on-one interviews for in-depth conversations and organize focus groups to encourage open dialogue. Utilize open-ended survey questions to collect written feedback, allowing team members to share their thoughts and ideas in their own words.
Next, assess employee sentiment and morale. Regularly measure the level of commitment, motivation, and satisfaction among your workforce through employee engagement surveys. Solicit opinions and observations during team meetings and observe day-to-day interactions among team members, noting any signs of tension, collaboration, or disengagement.
Lastly, evaluate team dynamics and collaboration. Review the effectiveness of communication tools and platforms, identify areas of conflict or tension, and examine the tools and processes used for collaboration to identify opportunities for improvement or optimization.
Combining Hard and Soft Data for Better Insights
To gain better insights, foster increased engagement among team members. Encourage open sharing of opinions and experiences while acknowledging and celebrating the unique skills and achievements of each team member. Implement feedback loops for continuous improvement by establishing processes for regularly gathering, analyzing, and acting upon feedback from team members.
Achieve a holistic understanding of team performance by identifying strengths and areas for improvement, and considering both quantitative and qualitative factors. Both types of information contribute to a comprehensive understanding of team performance. Lastly, evaluate the impact of team dynamics on performance, considering factors like communication and collaboration to make informed decisions.
Benefits of Data-Driven Retrospectives
Data-driven retrospectives offer a plethora of advantages when integrated into your business processes. These benefits not only optimize team performance but also contribute to a healthy work environment.
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
By incorporating data-driven retrospectives, businesses can experience:
Improved information sharing among team members, leading to better decision-making.
Streamlined collaboration, enabling the team to work together towards common goals.
The establishment of a culture that values open dialogue and constructive feedback.
Increased Transparency and Trust Within the Team
Data-driven retrospectives contribute to a transparent work environment, resulting in:
Greater trust among team members, as they gain insights into their colleagues' contributions and challenges.
A more open atmosphere where employees feel comfortable sharing their concerns and ideas.
Reduced risk of miscommunication and misunderstandings, leading to more effective collaboration.
Early Identification of Issues and Process Improvements
By utilizing data-driven retrospectives, businesses can:
Detect potential problems or inefficiencies before they escalate.
Identify areas for improvement in processes or workflows.
Encourage proactive problem-solving and continuous optimization of existing processes.
Continuous Learning and Development
Data-driven retrospectives foster an environment where teams can:
Learn from past experiences and apply insights to future projects.
Reflect on individual and team performance, driving personal and professional growth.
Stay adaptable in the face of change, ensuring the team remains agile and responsive to evolving business needs.
Conclusion
In the data-driven era, retrospectives have become an indispensable tool for modern businesses. They foster collaboration and continuous improvement and ultimately lead to better business outcomes. Don't miss the opportunity to harness the power of data-driven retrospectives for your organization.
To get started, explore the various retrospective templates available here. These templates will help you design effective and engaging retrospectives tailored to your team's needs, propelling your business toward success.
Kick-start your organization’s use of retrospectives and start seeing improvements across departments, projects, and proccesses almost immediatley!
Reach out today and one of our experts will help build a product demo customized to your organization’s workflows to help you get started on the right foot.
About the author:
A programmer by trade, Nick Saraev is a freelance writer and entrepreneur with a penchant for helping people excel in their careers. He's been featured on Popular Mechanics & Apple News, and has founded several successful companies in e-commerce, marketing, and artificial intelligence. When he's not working on his latest project, you can find him hiking or painting.